Introduction
AI is rewriting the rules of how we build and test software. From automated test execution to AI-generated test cases and self-healing scripts, today’s QA landscape is transforming at lightning speed. With this rapid shift, a growing belief has emerged across teams and social platforms: “Manual testing is outdated. AI can do it all.”
But here’s the surprising truth — and the part most people overlook:
AI doesn’t replace software testing fundamentals; it depends on them.
Without strong basics, automation breaks. Without solid understanding, AI generates wrong or incomplete test scenarios. And without human reasoning, even the most advanced tools miss real-world issues that impact users.
Think of it this way: AI can accelerate testing, but only a tester with strong fundamentals can guide it, correct it, and validate whether its results actually make sense. Whether you’re a new QA tester or an experienced professional, mastering the basics of software testing remains the foundation for building reliable, secure, user-friendly software in an increasingly automated world.
In this blog, you’ll discover why fundamentals are becoming more important — not less — how they empower AI-driven testing, and what QA testers must know to stay future-ready in a landscape where technology evolves daily.
What Are Software Testing Basics?
Before exploring AI-driven testing, it’s important to understand what “software testing basics” actually mean. These are the core principles, techniques, and thought processes that ensure a product works the way it should — under real-world conditions, for real users, across different devices and scenarios.
At its heart, software testing basics are the foundation of quality assurance. They help QA testers think clearly, test logically, and uncover issues that automation or AI alone might miss.
These fundamentals include:
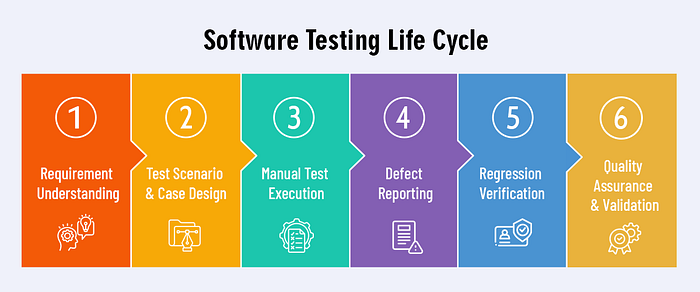
- Understanding project requirements
Knowing what the product should do, what the users expect, and what business goals the software must meet - Creating strong test scenarios and test cases
Well-written test cases guide both manual and automated testing. Poorly written ones cause bugs to slip through unnoticed. - Executing manual tests carefully
Manual testing remains essential for usability checks, UI validation, exploratory testing, and real-human behavior analysis. - Reporting bugs clearly
A clear bug report saves developers hours of effort and prevents misunderstandings in cross-functional teams. - Performing regression testing
Every new feature update can break existing functionality. Regression testing ensures nothing gets unintentionally damaged. - Ensuring stability, usability, and functionality
The basics ensure that software isn’t just “working” — it’s stable, user-friendly, and reliable.
These are not optional skills — they’re the building blocks of every testing approach, including Artificial Intelligence (AI)-assisted testing. Automation may reduce effort, but it cannot replace a tester’s understanding, intuition, and analytical ability.
Real-world failure example:
Imagine this:
An automated test suite runs overnight, and every test passes. The team feels confident and pushes the release live. But users immediately complain that the “Checkout” button is confusingly placed and doesn’t respond on certain screen sizes.
Why did this happen?
Because the test cases were incomplete — they checked functionality but ignored usability scenarios. Automation simply executed what it was told.
Only testers with strong fundamentals would have identified the issue beforehand.
Why Software Testing Still Matters
The Misconception: “AI and Automation Replace Manual Testing”
With the rise of high-speed automation tools and AI-generated test cases, it’s easy to believe that manual testing is becoming unnecessary. Many assume:
Automation + AI = No testers needed.
But the reality is very different.
AI still cannot fully understand:
- Human emotions, intuition, or behavior patterns
- User frustration or confusion
- Unexpected real-world edge cases
- Visual alignment, UI glitches, or UX flaws
- Situations where users behave differently than expected
Automation is powerful — but it is limited to what you script or instruct it to check.
It cannot think like a user.
It cannot question requirements.
It cannot adapt to new scenarios unless humans design those scenarios.
This is why AI doesn’t replace testers — it changes the role of testers.
Instead of doing repetitive tasks, QA professionals now:
- Review and validate AI-generated test cases
- Interpret results and understand failures
- Bring human insight into usability, accessibility, and user experience
- Design smarter testing strategies that AI can assist with
In other words, AI makes basic QA skills more important than ever.
The Importance of Software Testing
Software testing is the backbone of any successful digital product. It ensures that an app or website works smoothly, securely, and consistently — long before users interact with it. Even with AI and automation becoming more common, software testing remains essential because it prevents failures, protects user experience, and strengthens product reliability.
Testing helps catch issues early, reduces the risk of costly bugs, and ensures the software performs well across different devices, browsers, and real-world scenarios. It also plays a crucial role in security by identifying vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Software testing matters because users expect perfection — and even one small bug can break trust. Whether manual, automated, or AI-assisted, strong testing practices ensure your product is stable, safe, and ready for real-world use.
Real-World Examples That Prove Why Software Testing Cannot Be Ignored
Even the world’s biggest brands have faced serious consequences due to missing or inadequate testing. Here are a few real incidents:
1. Flipkart’s “Big Billion Day” Crash (2014)
A massive traffic spike caused website downtime, order failures, and pricing glitches — forcing Flipkart to issue a public apology.
2. Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS) Payment Failure (2015)
A software bug prevented 600,000+ transactions from being processed, leading to a £66 million regulatory fine.
3. Yahoo Data Breach (2016)
A vulnerability exposed 500 million user accounts, becoming one of the largest security breaches in history.
4. Okta Security Incident (recent)
A software bug led to a major authentication system breach, impacting customer data and damaging the company’s reputation.
These incidents highlight a simple truth: even one untested feature, bug, or security flaw can cost millions — and break user trust overnight.
Manual vs Automated vs AI Testing: What’s the Real Difference?
As testing evolves, many QA testers wonder which approach is “best.” The truth is — all three have different strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases. Instead of competing, they work together to deliver higher-quality software.
Types of Software Testing
Software testing comes in many forms, but most methods fall into two broad categories: functional and non-functional testing.
Understanding these two categories gives beginners and QA testers clarity on what is being tested and why it matters — especially when working alongside automation or AI tools.
Below is a fresh, expanded, and unique breakdown suitable for your blog.
Functional Testing
Functional testing focuses on what the software should do.
It ensures every feature, button, workflow, and user action behaves exactly the way requirements describe. This type of testing is all about behavior, accuracy, and expected outcomes.
1. Unit Testing
This is the first and smallest level of testing.
It focuses on individual functions, methods, or components in isolation. Developers run unit tests to catch small issues early — before those pieces interact with the rest of the system. Stronger unit testing often results in fewer bugs later during integration or system-level tests.
2. Integration Testing
Once individual components work well independently, integration testing checks whether they work well together.
A simple example:
Does the frontend properly interpret API responses?
Does the database return the right output when multiple services access it?
This step prevents unpredictable failures that only occur when modules interact.
3. System Testing
Here, the entire application is tested as a complete, integrated system.
It verifies not just individual features but how they work in real scenarios — from login to checkout, from data entry to reporting.
System testing helps teams understand whether the product meets functional expectations end-to-end.
4. Acceptance Testing (UAT)
This is where real users, business owners, or stakeholders test the product with real-world use cases.
They verify whether the software delivers true business value — not just whether it works technically.
UAT is the final confirmation step before a release, ensuring the product solves the right problem in the right way.
5. Regression Testing
Any time developers add new features, fix bugs, or make improvements, there’s a risk of breaking existing functionality.
Regression testing ensures everything that previously worked still works.
It is one of the most crucial testing types in continuous development environments.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing focuses on how well the software performs rather than what it does.
It evaluates quality attributes like speed, security, stability, and user experience — areas automation and AI often assist with, but human insight remains essential.
1. Performance Testing
Performance testing measures how the application behaves under normal and extreme loads. It answers questions such as:
- How fast does the page load with 1,000 users?
- Does the system slow down when data increases?
- Can the application scale without breaking?
This is crucial for user satisfaction and platform reliability.
2. Security Testing
Security testing attempts to uncover vulnerabilities that could expose data, compromise users, or allow unauthorized access.
Testers simulate attacks, misuse, or manipulation to ensure the system is protected.
With cyber threats rising, this type of testing has become indispensable.
3. Usability Testing
Usability testing focuses entirely on the user experience.
It checks how easy, intuitive, and comfortable the software feels — from navigation and readability to error messages and overall flow.
A product that is technically perfect but difficult to use will still fail users, making this form of testing extremely important.
4. Compatibility Testing
Today’s users access software on countless devices and browsers. Compatibility testing ensures the product works well everywhere:
- Windows, macOS, Linux
- Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Edge
- Mobile devices, tablets, desktops
This avoids issues where users on specific devices encounter errors others never see.
5. Reliability Testing
Reliability testing verifies that the application can run continuously over a period of time without unexpected crashes or failures.
It measures how stable and consistent the software is during long-term usage, heavy processing, or repeated operations.

Key Testing Methods: A Look Under the Hood
Understanding software testing is not just about what you test — it’s also about how you test it.
Different testing methods depend on how much knowledge the tester has about the internal structure and logic of the application. These methods shape the way test cases are designed, executed, and interpreted.
White-Box Testing
White-box testing involves full visibility into the application’s internal code, logic, and architecture.
Testers (often developers) use this method to:
- Validate code paths
- Check for logical errors
- Ensure conditions, loops, and exceptions work correctly
- Detect inefficiencies and hidden vulnerabilities
It is commonly used in unit testing and early development stages where deep code-level insights matter.
Black-Box Testing
Black-box testing requires no knowledge of how the underlying system is built.
Testers behave exactly like real users — interacting only with the visible UI, inputs, and outputs.
This method helps teams evaluate:
- Core functionality
- User workflows
- Error handling
- Input/output behavior
- Overall user experience
Most system, regression, and acceptance testing fall into this category.
Grey-Box Testing
Grey-box testing is a blend of both approaches. The tester has partial knowledge of the internal logic (e.g., database structure, API behavior, architectural flow) but still tests from a user-centered viewpoint.
This hybrid method offers the best of both worlds:
- Better prediction of edge cases
- More meaningful test scenarios
- Higher accuracy in finding hidden defects
- Stronger test coverage
Modern AI-driven tools also use a grey-box approach — combining interface-level interactions with structural understanding to generate more intelligent and resilient tests.
Dive into the full blog here → https://www.logicspice.com/blog/why-software-testing-basics-matter-even-with-ai-and-automation

Comments
Post a Comment